Understanding SATA definitions and facts is critical for computer learning. SATA (Serial ATA) is a standard for connecting hard disk drives and other storage devices to motherboards. It was developed by Intel in 2002 as part of its Serial ATA technology initiative. Today, SATA is ubiquitous on desktop and laptop computers as well as servers.
SATA has been a round for a long time and has gone through many changes during it development, with a number of newer versions from the original. This attitude keeps SATA as an integral part of computing despite the challenges from newer technologies that are faster offering much wanted performance.
If you want to know more about what is SATA, SATA port, SATA connection, SATA speed, SATA II, SATA Connector sizes, what is SATA 3 and the purpose of SATA, you should keep reading as we will cover all of these things.
What is SATA?
What is SATA? SATA (Serial ATA) is a storage technology that uses the parallel interface in computers. It has replaced the traditional serial ATA connector which was used on older hard drives. SATA offers a high performance data link between the computer and hard drive, which makes accessing your data faster and easier.
This makes it easier to manage your data, and it also reduces the amount of cabling that needs to be installed in your computer. It is very likely that the PC you are using still using some level of SATA technology.
SATA Port
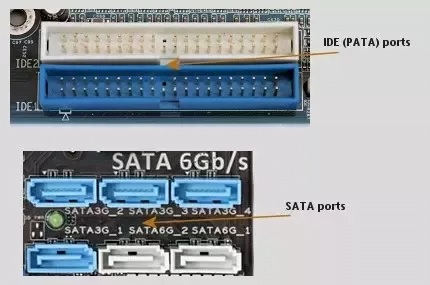
SATA ports are a popular option for attaching external hard drives and other peripherals to a computer. They offer high-speed data transfer, making them an ideal choice for connecting larger storage devices.
However, not all SATA ports are created equal. Some are much more robust than others, and can handle more stress and strain than others. If you’re considering purchasing a new external storage device, it’s important to select the right port for your needs.
Selecting the right SATA port can be tricky, but it’s worth it in the end. By ensuring that you select the right port, you’ll get maximum performance from your external storage device.
SATA ports are also commonly used for installing software or updates. Because they are connected to the motherboard, installing software or updates is fast and easy. Additionally, because SATA ports are commonly used, they are often in good condition.
SATA Connection

A SATA connection is a connection between two devices that uses the Serial ATA bus. A SATA connection is faster than a USB connection, and it’s also more reliable.
If you’re using a laptop, you might want to consider installing a SATA connection card instead of a USB one. You can also use a SATA connection to connect an external hard drive to your computer.
SATA tops the list of hard drive connection options when it comes to speed and reliability. SATA provides a higher bandwidth than USB 3.0, which is great for transferring large files.
You will find SATA connection inside the PC and not externally, which is the main reason why they will work faster than many external connections.
Purpose of SATA
The purpose of SATA was to replace Parallel ATA so that computers could become faster and more efficient. SerialATA was first introduced in 1999 as an upgrade to the Parallel ATA standard, and it offered a variety of benefits over its predecessor.
One of the key advantages of SerialATA is that data can be read from and written to devices more quickly than with ParallelATA. This is because SerialATA uses a faster signaling protocol than ParallelATA, which allows for more transactions to take place between devices per second.
Additionally, SerialATA supports higher capacities than ParallelATA, which makes it more suited for storing large files.
SerialATA provides enhanced error detection and correction capabilities compared to ParallelATA and handles much more devices than its predecessor.
SATA Speed
When it comes to storage, speed is of the essence. SATA (Serial ATA) is one of the most common bus systems used in modern PCs, and its high performance makes it a great choice for your data storage needs.
SATA can deliver up to 6 Gbps transfers depending on version, which is more than enough bandwidth to handle even the most demanding tasks. And because SATA has no moving parts, it’s incredibly reliable. Plus, since SATA ports are located near the motherboard, you’ll get superior performance compared to alternatives like USB 3.0 or Thunderbolt 2.
The speed that your SATA offers will depend on as mentioned the version of SATA you have and the components that make up your PC.
SATA II
Since its introduction in 2003, SATA II had quickly become the industry standard for connecting high-performance storage devices to computer systems. It offered a number of significant benefits over its predecessor, including increased data throughput and compatibility with more devices.
The main improvements over SATA include increased data throughput and compatibility with more devices. SATA II supports up to 6 Gbps data transfer rates and can support up to two host devices plus eight internal storage devices. This made it perfect for use with high-performance storage drives such as SSDs (solid state drives).
One potential application for SATA II is in gaming systems. With its increased data throughput, it can help reduce lag time between video frames and game play. It can also help improve overall system performance by allowing for faster loading times and larger saved games files.
SATA II is also commonly used in desktop systems where plenty of hard drive space is available but not necessarily required for extra functionality or performance. By using a separate hard drive for storage purposes, users can free up more space on their primary system drive.
What is SATA 3
SATA 3 is the latest and most advanced SATA standard for connecting hard drives and other storage devices to computers. It’s three times faster than SATA 2, making it perfect for high-speed data transfers.
It was released in 2007 and is probably the most popularly used SATA connection on modern computers until something better comes. Additionally, SATA 3 supports features like multi-word DMA and Native Command Queuing, which helps improve overall performance.
And because it uses a different bus protocol than SATA 2, you can also connect legacy devices to a new SATA 3 port without any software updates or compatibility issues.
This makes it perfect for high-speed storage solutions, such as hard drives and SSDs. If you’re looking to upgrade your computer’s storage capacity, or want to use newer, faster hard drives without upgrading your entire system, SATA 3 is the way to go.
SATA Versions
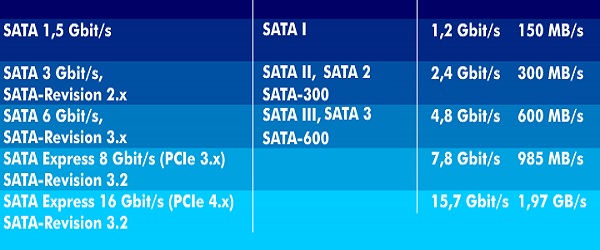
SATA versions are a key part of any computer system. There are a variety of different versions available on the market today. Below is a list of what them:
SATA 1 is the oldest connector type and it’s the weakest. It can only connect devices to the motherboard with a single cable, which can be limiting.
SATA 2 is better than SATA 1 because it can connect two devices at once with a single cable. However, it’s also more expensive than SATA 1.
SATA 3 is the latest connector type and it offers the highest speed possible. It can connect up to six devices at once with a single cable, making it ideal for large storage drives.
SATA-600 is a special version of SATA 3 that offers faster speeds than regular SATA 3. It’s also known as M-SATA because it uses the same mini-connector as IDE (internal expansion) hard drives.
SATA Express 8Gbps is an upgraded version of SATA-600 that offers faster speeds than regular SATA 3 and supports data transfers up to 8 gigabytes per second.
SATA Express 16Gbps is an even higher-speed version of SATA-Express that supports data transfers up to 16 gigabytes per second.
SATA Connector Sizes
A SATA connector is the most common type of connector used on hard drives and other portable devices. There are three sizes of connectors available: 3.5-inch, 2.5-inch, and 1.8-inch. The different sizes allow for different device capacities and connections.
3.5-inch SATA connectors are the most common size, and they come in both male and female varieties. They can support up to 8TB of storage space per drive. 2.5-inch SATA connectors are smaller than 3.5-inch connectors.
They can still hold a lot of data – up to 4TB per drive – and they’re also more common on portable devices like external hard drives and USB flash drives. 1.8-inch SATA connectors are the smallest size available and they’re used on some small internal laptop storage drives and solid state drives.
When it comes to connecting your SATA devices, be sure to know the size of the connector on each device. This will ensure compatibility and ensure a smooth connection.
How does SATA work?
Serial ATA (SATA) is a storage technology that uses a small number of pins on the motherboard to communicate with internal storage devices.
This communication is achieved through the use of Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA) controllers, which are integrated into motherboards. The SATA controller manages the flow of data between the hard drive and the motherboard.
The SATA interface is based on the parallel ATA standard, but it has been modified to improve performance. The SATA protocol supports three different transfer modes: AHCI, RAID 0, and RAID 1.
In AHCI mode, the SATA controller manages all disk access for devices attached to the motherboard. In RAID 0 mode, multiple hard drives are installed onto one motherboard and are treated as a single unit.
Data is striped across all drives in this configuration, and performance is improved because there is no need to read data from multiple locations on the hard drive. In RAID 1 mode, each hard drive is treated as an individual unit and data can be spread across both drives in order to improve performance.
What is SATA Protocol?
SATA protocol is a set of rules and standards that allow data to be transferred between devices on a computer system. The protocol helps organize the flow of information between devices, making it easier for the computer to read and write data.
SATA is unique in that it can support both hard disk drives and optical discs. This makes it an ideal solution for installing operating systems and applications, as well as storing large files. In addition,
It can also be used to transfer data between peripheral devices and the motherboard.Overall, SATA protocol is an important tool for modern computing systems. By ensuring seamless data flows between devices, SATA helps make your computer work faster and smoother.
How Do I Identify SATA 1 2 3?
To identify SATA 1 SATA 2 SATA 3 hard drives and SSDs. It is important to know the difference between these drive types in order to choose the correct one for your needs.
SATA 1 refers to older, slower hard drives that use a 3-pin connector. SATA 2 is the newer standard that uses a 6-pin connector and supports faster speeds. SATA 3 is the latest standard and uses a 9-pin connector, which allows for even faster speeds.
It is important to remember that not all drives are compatible with all ports on your computer. Before choosing a drive, make sure to check which port on your computer it will fit into. Also, be aware of the size of the drive; certain ports may not be able to accommodate larger drives.
What are the Two Types of SATA?
There are two types of SATA: hard drives and solid state drives. Hard drives use spinning disks to hold your data, while SSDs use flash-memory chips to store your data.
The main difference between the two is that hard drives are more durable and require a spinning disk to work, while SSDs are much faster and can be installed in places where a hard drive would not fit. However, SSDs are not as durable as hard drives and may not last as long.
Final Thoughts On SATA Definitions and Facts
We conclude that our explanation of SATA definitions and facts should help anyone better understand the how, what, and why of SATA technology. Understanding more about SATA its use and purpose an give you a greater appreciation for this device.
Be sure to read all the information above to better understand and use such technology, you will be glad you did.

